
Risk factors for papilledema are those that raise intracranial pressure as mentioned above. The mechanism of Idiopathic intracranial hypertension is not clearly understood however proposed mechanisms include increased venous sinus pressure from venous sinus stenosis, and reduced absorption to name a few. The time course for development of papilledema may be weeks if there is only a slow and mild rise in intracranial pressure, but severe and rapid changes in pressure can cause papilledema to present within a few hours to a day. colloid cyst obstructing the foramen of Monroe) When there is obstruction of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow (e.g.tumor, hemorrhage), or brain edema ( e.g.
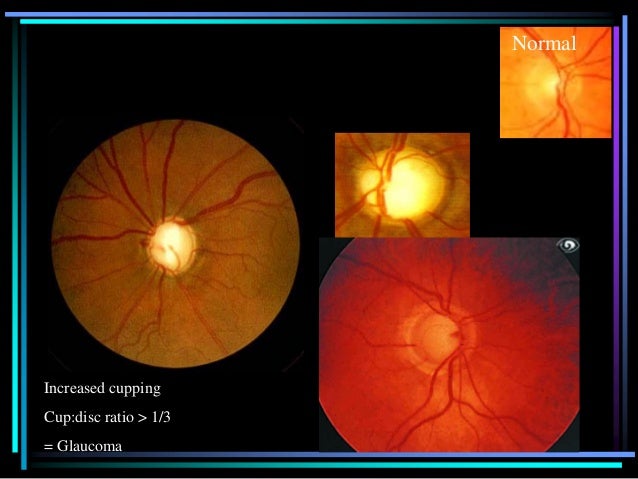

Normal ICP is typically less than 250 mm of water in adults when measured with a manometer and is less than 280 mm of water in children. Since the root cause of papilledema is increased intracranial pressure (ICP) this is an alarming sign which may presage such entities as brain tumor, CNS inflammation, cerebral venous thrombosis, or idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH).Īs noted above, papilledema is due to increased intracranial pressure from any cause. Papilledema must also be distinguished from pseudo-papilledema such as optic disc drusen. It must be distinguished from optic disc swelling from other causes which is simply termed "optic disc edema". Papilledema is a term that is exclusively used when a disc swelling is secondary to increased intracranial pressure (ICP).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
